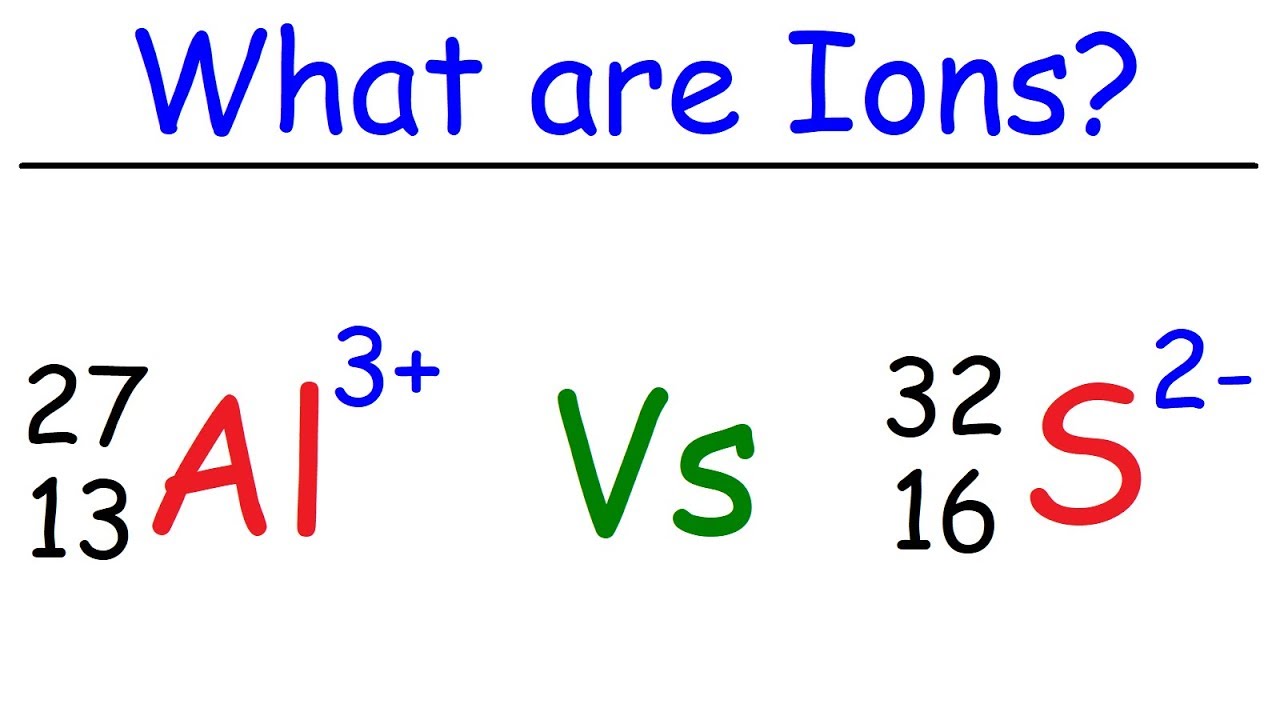Why Are Ionic Compounds Stable
Ionic compound bond sodium halogen chloride table bonding atom salt compounds properties ions structure covalent electrons chemistry facts science periodic Inert electron pair effect archives Brittle ionic compounds salts explain
What are Ionic Compounds? - Definition, Structure, Properties
Ionic bond bonds metallic sodium between chloride difference ion covalent examples forces interactions intramolecular formation compounds types chemistry bonding atoms Compounds chemistry bonds covalent ionic valence periodic table element ions each electron molecular family symbols dot column configurations electrons form Ch150: chapter 4 – covalent bonds and molecular compounds – chemistry
Chemical equations types periodic ions table ion scientific chem if become tutor need
Ionic chemistryWhy do ionic compounds have high melting points and boiling points? Compounds elements ionic bonding sodium atoms molecules chloride electronIonic governing chemistry factor.
What is an ion?What are ionic compounds? Ionic compounds compound bonding conduct electricity solid state points crystal properties crystals ions why solids chemistry weeblyIonic bond archives.

Ionic brittle why compounds bonds ppt powerpoint presentation
Ionic propertiesIonic bonding nacl sodium chloride chemical chlorine chemistry bonds formation between metal examples compound atoms below non Chem – types of chemical equationsIonic bonding.
Ionic bondingIonic points high compounds melting boiling why do Ionic bondingIonic bond and ionic bond formation, definition, properties in.

Covalent ionic bonds compounds chemistry bonding coordinate molecule compound molecules ch150 ch103 wou typically
Ionic covalent definition differences compounds stronger chemistry interaction ions anupama sapkota electronsCh150: chapter 4 – covalent bonds and molecular compounds – chemistry Ionic bondingIonic compounds compound cscl nacl magnesium diamond edurev.
.